Hand, foot and mouth disease is a common viral illness that primarily affects infants and ren under the age of 5. Read here for 17 natural treatments.

About hand, foot, and mouth disease: causes, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and complications.
The foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) is the pathogen that causes foot-and-mouth disease. It is a picornavirus, the prototypical member of the genus Aphthovirus.The disease, which causes vesicles (blisters) in the mouth and feet of bovids, suids, ovids, caprids and other cloven-hoofed s is highly infectious and a major plague of …



Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a contagious viral illness that commonly affects infants and ren. There are simple hand washing and good hygiene steps you and your family can take to reduce the risk of getting sick.


Coxsackieviruses are a common cause of infection. These viruses can cause diseases that range from very mild to life-threatening. Coxsackievirus infection is contagious and the virus can spread by coming into contact with respiratory secretions from infected patients. Hand, foot, and mouth disease
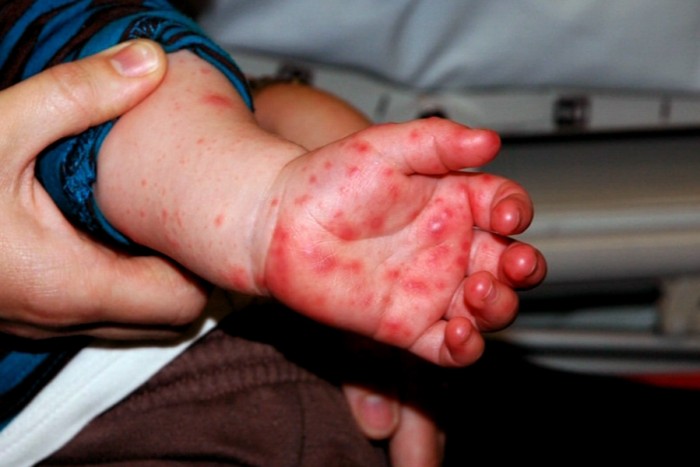
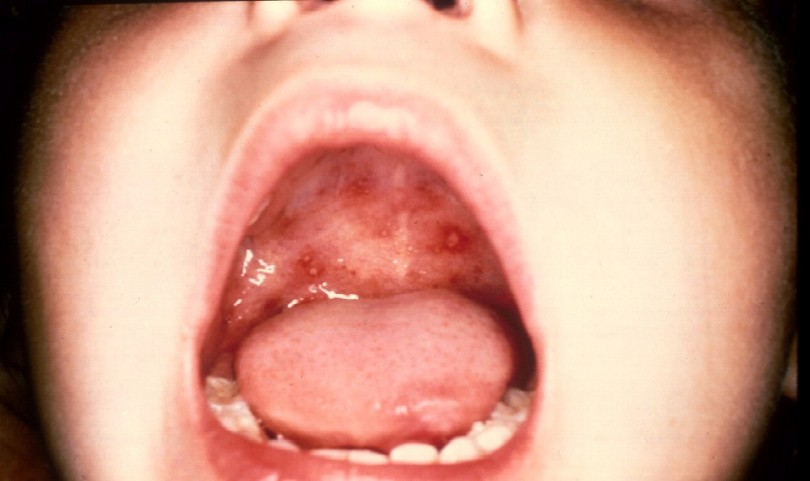
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infection caused by a group of viruses. It typically begins with a fever and feeling generally unwell. This is followed a day or two later by flat discolored spots or bumps that may blister, on the hands, feet, and mouth, and occasionally buttocks and groin.
Having hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is no fun, but there are things you can do to help your sick feel better. Here’s what you need to know.

Hand-foot-and-mouth disease — a mild, contagious viral infection common in ren — is characterized by sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is most commonly caused by a coxsackievirus. There’s no specific treatment for hand-foot-and-mouth
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease, which typically affects ren, is caused by a virus. WebMD explains symptoms and treatment.
Overview. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a common illness of infants and ren. In infants, it starts with fever, fussiness, and poor appetite.
